4. Methods
The review protocol was conducted in line with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (see S1 Checklist).
Search strategy and selection process
A systematic search was conducted up until April 2023 from two sources of database, PubMed and PsycINFO, using a range of terms relevant to the title and research questions (see full list of search terms in S1 Appendix). All the searched articles can be accessed in the S1 Data. The eligible articles were selected according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Inclusion criteria used for the present review were:
▪ (i) participants in the studies with clinical diagnosis of Internet Addiction;
▪ (ii) participants between the ages of 10 and 19;
▪ (iii) imaging research investigations;
▪ (iv) works published between January 2013 and April 2023;
▪ (v) written in English language;
▪ (vi) peer reviewed papers and
▪ (vii) full text.
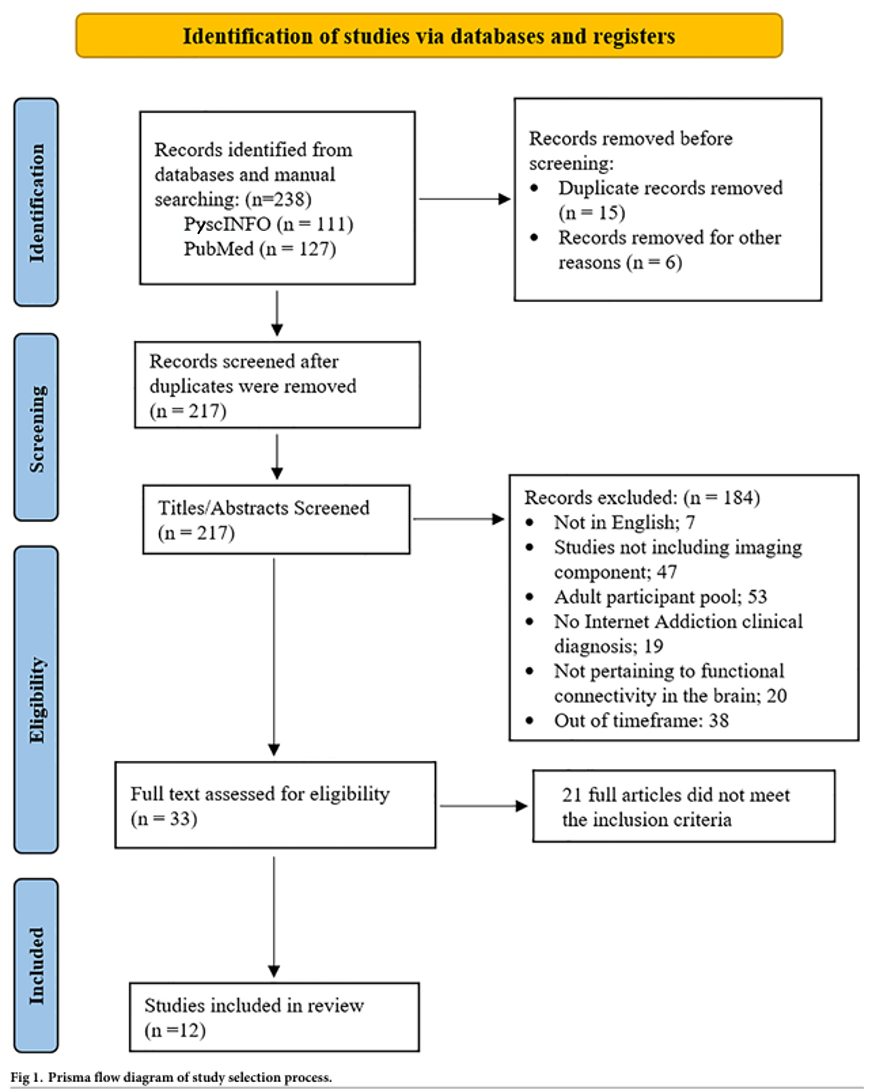
The numbers of articles excluded due to not meeting the inclusion criteria are shown in Fig 1. Each study’s title and abstract were screened for eligibility.
Quality appraisal
Full texts of all potentially relevant studies were then retrieved and further appraised for eligibility. Furthermore, articles were critically appraised based on the GRADE (Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations) framework to evaluate the individual study for both quality and bias. The subsequent quality levels were then appraised to each article and listed as either low, moderate, or high.
Data collection process
Data that satisfied the inclusion requirements was entered into an excel sheet for data extraction and further selection. An article’s author, publication year, country, age range, participant sample size, sex, area of interest, measures, outcome and article quality were all included in the data extraction spreadsheet. Studies looking at functional connectivity, for instance, were grouped, while studies looking at functional connectivity in specific area were further divided into sub-groups.
Data synthesis and analysis
Articles were classified according to their location in the brain as well as the network or pathway they were a part of to create a coherent narrative between the selected studies. Conclusions concerning various research trends relevant to particular groupings were drawn from these groupings and subgroupings. To maintain the offered information in a prominent manner, these assertions were entered into the data extraction excel spreadsheet.